# Data Governance for AI Systems </br> ## based on GDPR & EU AI Act guidelines </br> Author - <u><a href="https://www.kunal-pathak.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Kunal Pathak</a></u> --- # Focus - Explore the impact on Data Governance in AI/ML activities due to: - the GDPR Act and - the EU AI Act Note: --- # Agenda - Summarize GDPR and EU AI Act regulatory requirements. - Discuss their impact on data governance of AI/ML systems. - Provide practical guidance for responsible data handling in AI/ML Lifecycle. --- # Overview | Aspect | GDPR | EU AI Act | | --------------- | ---------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------- | | Focus | Personal data protection and privacy | Governance of AI systems | | Scope | All personal data processing | AI systems, especially high-risk ones | | Fully effective | 2018 | 2026 | | Requirements | Data minimization, purpose limitation, consent | Risk assessment, transparency, human oversight | --- # EU AI & GDPR Acts - **The EU AI Act builds upon GDPR**: - Extends GDPR's risk-based approach to AI systems - Enhances transparency requirements for AI decision-making - Emphasizes AI-specific data quality and rights protection - Expands accountability to AI providers and users - **Complementary regulations** - The EU AI Act does not contradict the GDPR Act. - Rather it builds upon GDPR's foundation to address the specific challenges posed by artificial intelligence. --- # Timelines </br> <a href="https://kanad13.github.io/EU-AI-Act/decks/EU_AI_Act-timelines.html" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Click here for an iterative view of the timelines.</a> Note: - 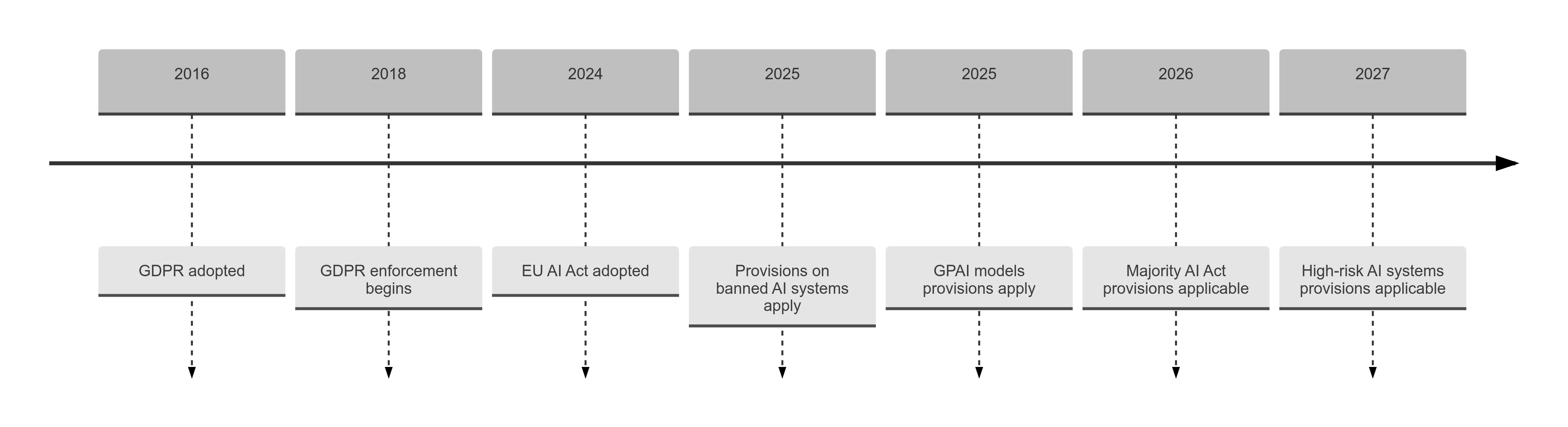 --- # GDPR + EU AI Act - GDPR lays the groundwork for data protection; the AI Act expands with specific AI requirements. - GDPR targets general data processing, while the AI Act tackles AI-specific challenges. - GDPR covers all personal data; the AI Act zeroes in on AI systems. - The AI Act introduces AI risk categories and human oversight needs. --- # Impact on Data Governance This section examines six key aspects of data governance in response to these regulations: 1. **Data Collection and Consent**: Ensures lawful and transparent data collection. 2. **Data Quality and Preparation**: Addresses biases and errors in data handling. 3. **Data Security and Access Control**: Protects sensitive ML model information. 4. **Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation**: Balances ML data needs with privacy principles. 5. **Data Transparency and Explainability**: Builds trust and enables AI system oversight. 6. **Data Subject Rights**: Ensures individual autonomy and control in AI decisions. --- ## 1. Data Collection and Consent - **Purpose** - Ensure lawful data collection and processing with authorization from data subjects. - **Regulatory Requirements** - `GDPR Article 6`: Lawful bases for data processing - `GDPR Article 7`:Explicit consent for ML training. - `GDPR Articles 13-14`: Clear information on data collection, purpose, and rights. - `GDPR Article 35`: Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk AI use cases. - `EU AI Act Article 10`: Data governance for high-risk AI systems. - **Practical Steps** - Identify lawful data processing basis (e.g., consent, legitimate interests). - Develop concise consent forms for ML training. - Create transparent privacy notices for data use in ML. - Implement a DPIA process for high-risk ML projects. --- ## 2. Data Quality and Preparation - **Purpose** - Ensure high-quality, unbiased data for accurate ML models. - **Regulatory Requirements** - `GDPR Article 5(1)(d)`: Accuracy and relevance of training data. - `EU AI Act Article 10(3)`: Address biases to prevent discrimination. - `EU AI Act Article 10`: Data validation and error handling. - **Practical Steps** - Implement data cleaning to remove errors. - Develop validation protocols for accuracy. - Conduct regular data quality audits. - Implement bias detection and mitigation. - Document data preparation steps. --- ## 3. Data Security and Access Control - **Purpose** - Protect data confidentiality and integrity. - **Regulatory Requirements** - `GDPR Article 32`: Technical and organizational safety measures. - `EU AI Act Article 12`: Logging and traceability. - **Practical Steps** - Use encryption for data at rest and transit. - Establish role-based access control (RBAC). - Apply pseudonymization techniques. - Implement secure storage and transfer protocols. - Set up logging and monitoring systems. --- ## 4. Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation - **Purpose** - Collect and use only necessary data. - **Regulatory Requirements** - `GDPR Article 5(1)(c)`: Data minimization. - `GDPR Article 6(4)`: Purpose limitation. - `EU AI Act Article 10`: Align data use with AI purpose. - **Practical Steps** - Conduct audits to remove unnecessary data. - Implement data retention policies. - Design models to minimize personal data use. - Regularly review and update data purposes. --- ## 5. Data Transparency and Explainability - **Purpose** - Ensure transparency in data use and model decisions. - **Regulatory Requirements** - `GDPR Article 15(1)(h)`: Explain AI decisions. - `EU AI Act Articles 11-13`: Record-keeping and traceability. - **Practical Steps** - Develop clear ML process documentation. - Implement data lineage tracking. - Use explainable AI techniques. - Create user-friendly model decision explanations. - Maintain and update AI documentation. --- ## 6. Data Subject Rights - **Purpose** - Respect and facilitate data subject rights in AI systems. - **Regulatory Requirements** - `GDPR Articles 15-22`: Data subject rights (access, rectification, erasure, etc.) - `GDPR Article 22`: Right not to be subject to solely automated decisions. - `EU AI Act Article 52`: Transparency obligations for certain AI systems. - `EU AI Act Articles 14, 29`: Human oversight & right to explanation for high-risk AI systems. - **Practical Steps** - Implement systems for handling data subject access requests. - Develop processes for data rectification and erasure in AI systems. - Create mechanisms to opt out of solely automated decisions. - Ensure AI systems can provide meaningful explanations for high-risk decisions. - Implement human oversight measures for high-risk AI systems. - Regularly train staff on handling data subject rights in AI context. --- # Best Practices - Document all data sources, types, and flows. - Develop data rectification and erasure processes. - Ensure AI systems explain automated decisions. - Form cross-functional compliance teams. - Implement data version control and traceability. - Train staff on governance and compliance. - Deploy technical solutions like DLP. - Conduct periodic internal audits. --- # Practical Examples - **Fair Data Preprocessing** - Example: Credit Scoring - Remove protected attributes like gender and race - Apply reweighing or prejudice remover algorithms - **Federated Learning** - Example: Healthcare Models - Train on decentralized data - Aggregate updates without central collection - **Explainable AI** - Example: Insurance Risk - Use interpretable models or SHAP values - Highlight feature importance and decisions - **Continuous Monitoring** - Example: Fraud Detection - Detect data drift - Automate retraining with oversight --- # Key Takeaways - Integrate data governance in AI/ML Lifecycle early. - Follow the GDPR and EU AI Act guidance for responsible data use. - Use a cross-functional approach combining legal, technical, and ethical aspects. - Prioritize continuous monitoring, auditing, and improvement in Data Governance practices. --- # Further Reading - **Quick introduction to the EU AI Act in 2 mins** - <a href="https://pdflink.to/eu-ai-act-kunal-pathak/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Learn More</a> - Iterative timeline for the EU AI Act - <a href="https://kanad13.github.io/EU-AI-Act/decks/EU_AI_Act-timelines.html" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Click here</a> - **How AI Act builds on GDPR** - <a href="https://github.com/kanad13/EU-AI-Act/blob/main/decks/EU_AI_Act.md#gdpr--eu-ai-act" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Learn More</a> - **Practical Guide to EU AI Act** - <a href="https://github.com/kanad13/EU-AI-Act/decks/EU_AI_Act.md" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Learn More</a> - **About the Author: Kunal Pathak** - <a href="https://www.kunal-pathak.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Portfolio Website</a> - <a href="https://github.com/kanad13" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">GitHub Contributions</a> - <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/kunal-pathak-profile/" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">LinkedIn Profile</a> --- # references - Full Text of the GDPR Act - <a href="https://eur-lex.europa.eu/EN/legal-content/summary/general-data-protection-regulation-gdpr.html" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">click here</a> - Full Text of the EU AI Act - <a href="https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32024R1689" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">click here</a> - Up-to-date developments and analyses of the EU AI Act - <a href="https://artificialintelligenceact.eu" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">click here</a> - Details from the European Parliament Think Tank - <a href="https://www.europarl.europa.eu/thinktank/en/document/EPRS_BRI(2021)698792" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">click here</a> --- # Important Note - The content in this repository includes material from official European Union publications, which is subject to the following copyright notice: © European Union, 1995-2024 - The information presented in this presentation regarding the GDPR & EU AI Acts is based on my personal understanding and interpretation. These insights and recommendations are my own and do not represent the official stance of any company, organization, or the European Union. - This presentation is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as legal advice. - For the most accurate and up-to-date information, please refer to official EU resources. - I am not afflicted in any way to the European Union. I am presenting this information as an individual interested in the topic. - No copyright infringement is intended. All legal rights belong to the EU. The material used in this presentation is for educational purposes and falls under fair use. - I bear no legal responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided in this presentation. - Companies and individuals should conduct their own research and consult with qualified legal & technical experts before implementing any compliance measures. --- ## Thank You </br> <u><a href="https://www.kunal-pathak.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Kunal Pathak</a></u>